Welcome To Zenthermik
Best Thermistors & Sensor Manufacturer In India
We are a trusted specialist in NTC Thermistor Sensors engineered for
Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Battery Management Systems (BMS).
Industries We Serve

Automobiles

Home Appliances

EV Battery

Air Conditioner

Refrigerator

Stabilizer
NTC Thermistors
Thermistor BasedProducts
About Us
Specialized NTC Thermistor Solutions for EV & Battery Management Systems (BMS)
Precision Temperature Sensing for Next-GenerationElectric Vehicles
We are a trusted specialist in NTC Thermistor Sensors engineered for Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Battery Management Systems (BMS). As EV powertrain and battery technologies evolve, the need for accurate, reliable, and robust thermal management becomes critical. Our advanced thermistor sensors are designed to monitor and control temperatures across high-performance lithium-ion battery packs, power electronics, charging systems, and electric motors.
Service 2026verified by TrustindexTrustindex verifies that the company has a review score above 4.5, based on reviews collected on Google over the past 12 months, qualifying it to receive the Top Rated Certificate.
Featured Products

Automotive Sensors

High Precision Beads

Automotive Sensors

Powder Coated Sensors

Screw Mounting Sensors

Sensors for Medical Applications
Why Zenthermik
Key Features of OurEV/BMS Thermistor Solutions
High Accuracy Temperature Sensing
Resistance tolerance as tight as ±1% (R25)
Fast Thermal Response
Ultra-quick reaction times for dynamic load conditions
Robust Encapsulation
Epoxy, Glass, and Overmolded Probes for moisture, vibration, and chemical resistance
Wide Operating Range
-40°C to +150°C (Higher ranges available on request)
Custom Lugs
Designed specifically for Laser Welding, Ultrasonic Welding, and Screw Mounting applications.
High Voltage Isolation
Specialized designs for HV battery packs and power modules
EV & BMS Applications
- Cell Temperature Monitoring (Cell Sensing Probes)
- Battery Module Thermal Control
- Cooling System Temperature Sensors
- Onboard Chargers (OBC) Thermal Management
- DC-DC Converters & Inverters Temperature Protection
- Motor & Powertrain Component Sensing
- Charging Connector & Cable Temperature Monitoring
Custom Solutions for EV Innovators
Our engineering team collaborates with EV manufacturers and Tier-1 suppliers to design custom NTC thermistor sensors optimized for the unique thermal management needs of electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a thermistor?
A thermistor is a type of temperature sensor made of semiconductor material whose resistance changes significantly with temperature.
What are the main types of thermistors?
• NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient): Resistance decreases as temperature increases.
• PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient): Resistance increases as temperature increases.
How does a thermistor work?
Thermistors rely on the temperature-dependent conductivity of semiconductor materials. A change in temperature alters the number of charge carriers, thus changing the resistance.
What is the typical temperature range for thermistors?
• Usually –55°C to +150°C
• Some special thermistors can measure up to 300°C
What are the advantages of using a thermistor?
✅ High sensitivity to temperature changes
✅ Compact size
✅ Fast response time
✅ Cost-effective
Where are thermistors commonly used?
• Temperature measurement and control (HVAC, medical devices)
• Battery packs (overheating protection)
• Automotive sensors
• Consumer electronics (e.g., air conditioners, refrigerators)
How do you read a thermistor’s resistance?
You measure the resistance with a multimeter and then use a temperature-resistance table or Steinhart–Hart equation to find the corresponding temperature.
What is the Beta (β) value of a thermistor?
It’s a constant that relates resistance to temperature, often used in the thermistor equation:
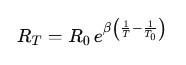
where:
• R(T) = resistance at temperature T (in Kelvin)
• R0 = resistance at reference temperature T₀ (usually 25 °C = 298.15 K)
• β = Beta value (in Kelvin)
If you know the thermistor resistance at two different temperatures, you can calculate β: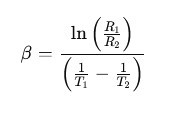
where:
• R₁ = resistance at T₁ (K)
• R₂ = resistance at T₂ (K)
Example Calculation
Suppose:
R₁ = 10 kΩ at 25 °C → T₁ = 298.15 K
R₂ = 3.3 kΩ at 50 °C → T₂ = 323.15 K
Ln (10 000/3300) =ln (3.03) ≈1.109
1/298.15−1/323.15=0.003354−0.003096=0.000258 
So, the Beta value is ~4300 K.
What is Steinhart Equation for thermistor?
The Steinhart–Hart equation is a more accurate model for an NTC thermistor’s resistance–temperature relationship:
1/T=A+Bln(R)+C(ln(R))3
where:
• T = temperature in Kelvin
• R = thermistor resistance (Ω)
• A, B, C = Steinhart–Hart coefficients (sensor-specific)
This is more precise than the simple Beta equation, especially over a wide temperature range.
How to Get the Coefficients (A, B, C)
You need three resistance–temperature points (R₁, R₂, R₃ at T₁, T₂, T₃).
1️⃣ Take the natural log of each resistance:
L1=ln(R1), L2=ln(R2), L3=ln(R3)
2️⃣ Compute the reciprocal of temperatures in Kelvin:
Y1=1/T1, Y2=1/T2, Y3=1/T3
3️⃣ Solve the simultaneous equations:
Y1=A+BL1+CL13
Y2=A+BL2+CL23
Y3=A+BL3+CL33
Solving gives A, B, C.
When to Use Steinhart–Hart vs Beta?
• Beta equation → simple, good for narrow range (~25–85 °C)
• Steinhart–Hart → more accurate across wide range (–50 to +150 °C)
How do thermistors compare to other temperature sensors (RTDs, thermocouples)?
• More sensitive than RTDs & thermocouples
• Less expensive
• Shorter temperature range
• More nonlinear response